Are you just starting to learn English and feeling confused about verb tenses? Don’t worry! Verb tenses are like the building blocks of sentences. They help us show when something happens, whether it’s now, in the past, or in the future. In this beginner-friendly guide, we’ll explore a verb tenses list with examples for beginners to make everything clear and easy to understand. We’ll break down the main tenses into past, present, and future categories, including simple, perfect, and continuous forms. Plus, we’ll include a handy verb forms chart and 20 examples of present, past, and future tenses to practice with.
As an English learner, mastering verb tenses will help you speak and write more confidently. Imagine telling a story about your day without mixing up “I eat” and “I ate”. It makes a big difference! This article is designed for beginners, so we’ll use simple words, short sentences, and lots of examples. By the end, you’ll have a solid grasp of past present future tenses, simple perfect continuous forms, and how to use them in everyday English.
Why focus on verb tenses? They are key to clear communication. Beginners often struggle with them because English has 12 main tenses, but don’t panic, we will explain each one step by step. We’ll also cover common mistakes and tips to avoid them. Let’s dive in and make learning fun!
What Are Verb Tenses? A Quick Overview for Beginners
Before we jump into the verb tenses list with examples for beginners, let’s define what verb tenses are. A verb tense tells us the time of an action or state. English verbs change form based on time: past (yesterday), present (now), or future (tomorrow).
For example:
- Past: I ate cheesecake.
- Present: I eat cheesecake.
- Future: I will eat cheesecake.
Each time has four aspects: simple (basic actions), continuous (ongoing actions), perfect (completed actions), and perfect continuous (ongoing and completed actions).
For example:
- Simple: “I walk.” (Basic habit)
- Continuous: “I am walking.” (Happening now)
- Perfect: “I have walked.” (Finished recently)
- Perfect Continuous: “I have been walking.” (Ongoing until now)
These combinations give us the 12 tenses. Don’t memorize them all at once but focus on one group at a time. In this guide, we’ll group them by past, present, future tenses to keep it organized. We’ll also include a verb forms chart later to show how verbs like “eat,” “go,” and “play” change.
Learning tenses helps with reading, writing, and speaking. For instance, in stories, you might switch from present to past to build excitement. Beginners can start with simple tenses and build up. Ready? Let’s start with the present tenses.

Present Tenses: Explaining Simple, Perfect, and Continuous Forms
The present tenses describe actions happening right now, habits, or general truths. They’re the easiest for beginners to start with. We’ll cover the four types: simple, continuous, perfect, and perfect continuous. Each includes structure, uses, and examples.
Present Simple Tense
The present simple is for habits, facts, or repeated actions.
Structure: Subject + base verb (add -s for he/she/it).
Uses:
- Daily routines: “I wake up at 7 AM.”
- Facts: “The sun rises in the east.”
- States: “She lives in New York.”
Examples:
1. I eat breakfast every morning. (Habit)
Common mistake: Don’t use it for actions happening right now but use present continuous for that.
Present Continuous Tense
This tense shows actions happening at this moment or temporary situations.
Structure: Subject + am/is/are + verb-ing.
Uses:
- Now: “I am reading a book.”
- Temporary: “She is staying with her aunt this week.”
- Future plans: “We are meeting tomorrow.”
Examples:
2. They are watching TV right now. (Current action)
3. I am learning English online. (Ongoing process)
Tip: Add “right now” or “at the moment” to practice this tense.
Present Perfect Tense
Present perfect connects past actions to the present, often with “just,” “already,” or “yet.”
Structure: Subject + have/has + past participle (e.g., eaten, gone).
Uses:
- Experiences: “I have visited Paris.”
- Recent actions: “She has finished her homework.”
- Unfinished time: “We have lived here for five years.”
Examples:
4. I have eaten lunch. (Finished recently)
5. He has lost his keys. (Effect now)
Beginners often confuse this with past simple But always remember, present perfect isn’t for specific past times like “yesterday.”
Present Perfect Continuous Tense
This emphasizes ongoing actions from past to now, often with “for” or “since.”
Structure: Subject + have/has + been + verb-ing.
Uses:
- Duration: “I have been studying for two hours.”
- Recent activity with results: “She has been running, so she’s tired.”
- Emphasis on process: “We have been waiting since morning.”
Examples:
6. I have been reading this book all day. (Ongoing)
7. They have been playing games for hours. (Duration)
Pro tip: Use this for actions that might continue, unlike perfect which focuses on completion.
To have a better understanding about the types of present tense please refer to the simplified table below.
| Types of Present Tense | Structure | Example Sentence |
| Simple Present | Subject + base verb (+s/es) | I eat breakfast at 7 a.m. |
| Present Continuous | am/is/are + verb-ing | I am eating breakfast right now. |
| Present Perfect | have/has + past participle | I have eaten breakfast already. |
| Present Perfect Continuous | have/has been + verb-ing | I have been eating breakfast for ten minutes. |

Past Tenses: Talking About Yesterday with Simple, Perfect, and Continuous
Now, let’s move by focusing on the past. These describe completed or ongoing actions before now. Great for storytelling!
Past Simple Tense
For finished actions in the past.
Structure: Subject + past verb (e.g., walked, ate).
Uses:
- Specific times: “I visited London last year.”
- Stories: “He opened the door and saw a surprise.”
- Habits: “She played piano as a child.”
Examples:
8. I walked to school yesterday. (Completed)
9. They ate dinner at 8 PM. (Specific time)
Avoid using with ongoing actions, save that for continuous.
Past Continuous Tense
Shows ongoing actions in the past, often interrupted.
Structure: Subject + was/were + verb-ing.
Uses:
- Background: “It was raining when I left.”
- Interrupted: “I was eating when the phone rang.”
- Parallel actions: “She was reading while he was cooking.”
Examples:
10. We were watching a movie at midnight. (Ongoing)
11. I was sleeping when you arrived. (Interrupted)
Tip: Combine with past simple for stories: “I was walking (continuous) when I saw (simple) a dog.”
Past Perfect Tense
For actions completed before another past action.
Structure: Subject + had + past participle.
Uses:
- Sequence: “I had finished before she came.”
- Regrets: “He had forgotten his wallet.”
- Stories: “By the time we arrived, the show had started.”
Examples:
12. She had eaten before the meeting. (Before another past)
13. We had seen that movie already. (Completed earlier)
This tense helps show order in the past—think “had” as “before past.”
Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Emphasizes ongoing actions before another past point.
Structure: Subject + had + been + verb-ing.
Uses:
- Cause: “I was tired because I had been working.”
- Duration: “They had been living there for years.”
- Emphasis: “She had been studying hard.”
Examples:
14. He had been running for an hour when it started raining. (Ongoing before)
15. We had been waiting since noon. (Duration)
For beginners, practice by adding “because” to explain reasons.
To have a better understanding about the types of past tense please refer to the simplified table below.
| Types of Past Tense | Structure | Example Sentence |
| Simple Past | Subject + past form of verb | I watched a movie last night. |
| Past Continuous | was/were + verb-ing | They were studying when I called. |
| Past Perfect | had + past participle | She had finished dinner before he arrived. |
| Past Perfect Continuous | had been + verb-ing | We had been waiting for an hour before the bus came. |

Future Tenses: Planning Tomorrow with Simple, Perfect, and Continuous
The future tenses predict or plan ahead. They use “will,” “going to,” or other helpers.
Future Simple Tense
For spontaneous decisions or predictions.
Structure: Subject + will + base verb.
Uses:
- Predictions: “It will rain tomorrow.”
- Promises: “I will help you.”
- Decisions: “I’ll call you later.”
Examples:
16. We will travel to Spain next year. (Plan)
Note: Use “going to” for planned futures: “I am going to eat.”
Future Continuous Tense
For ongoing actions in the future.
Structure: Subject + will + be + verb-ing.
Uses:
- At a specific time: “I will be sleeping at 10 PM.”
- Parallel: “She will be working while we eat.”
- Polite: “Will you be using the car?”
Examples:
17. I will be studying English tomorrow. (Ongoing)
18. They will be arriving soon. (Expected)
Great for schedules!
Future Perfect Tense
For actions completed by a future time.
Structure: Subject + will + have + past participle.
Uses:
- By a time: “I will have finished by noon.”
- Assumptions: “He will have arrived by now.”
- Milestones: “We will have lived here for 10 years.”
Examples:
19. She will have graduated by June. (Completed)
This shows completion in the future.
Future Perfect Continuous Tense
For ongoing actions up to a future point.
Structure: Subject + will + have + been + verb-ing.
Uses:
- Duration: “I will have been working for hours.”
- Cause: “She will be tired because she will have been traveling.”
- Emphasis: “We will have been practicing daily.”
Examples:
20. By next year, I will have been learning English for two years. (Duration)
Use for long futures.
To have a better understanding about the types of future tense please refer to the simplified table below.
| Types of Future Tense | Structure | Example Sentence |
| Simple Future | will + base verb | I will call you tomorrow. |
| Future Continuous | will be + verb-ing | She will be studying at 8 PM. |
| Future Perfect | will have + past participle | They will have finished the project by Friday. |
| Future Perfect Continuous | will have been + verb-ing | He will have been working here for five years next month. |
Ready for a change? See how our English speaking lessons for adults can transform your life.
Verb Forms Chart: A Quick Reference for Beginners
Here’s a verb forms chart. It shows base, past, past participle, and -ing forms for common verbs. Use this as a reference!
| Base Form | Present Form | Present Participle | Simple Past | Past Participle | Simple Future |
| eat | eat/eats | eating | ate | eaten | will eat |
| go | go/goes | going | went | gone | will go |
| play | play/plays | playing | played | played | will play |
| run | run/runs | running | ran | run | will run |
| write | write/writes | writing | wrote | written | will write |
| read | read/reads | reading | read | read | will read |
| speak | speak/speaks | speaking | spoke | spoken | will speak |
| sleep | sleep/sleeps | sleeping | slept | slept | will sleep |
| drive | drive/drives | driving | drove | driven | will drive |
| sing | sing/sings | singing | sang | sung | will sing |
| be | am/is/are | being | was/were | been | will be |
| have | have/has | having | had | had | will have |
| do | do/does | doing | did | done | will do |
| come | come/comes | coming | came | come | will come |
| see | see/sees | seeing | saw | seen | will see |
| get | get/gets | getting | got | got/gotten | will get |
| make | make/makes | making | made | made | will make |
| take | take/takes | taking | took | taken | will take |
| find | find/finds | finding | found | found | will find |
| know | know/knows | knowing | knew | known | will know |
Copy this chart and practice changing sentences. For irregular verbs like “go,” memorize the forms.
To summarize all the 12 main tenses, below is a colorful chart with the structure and example sentence of each type.
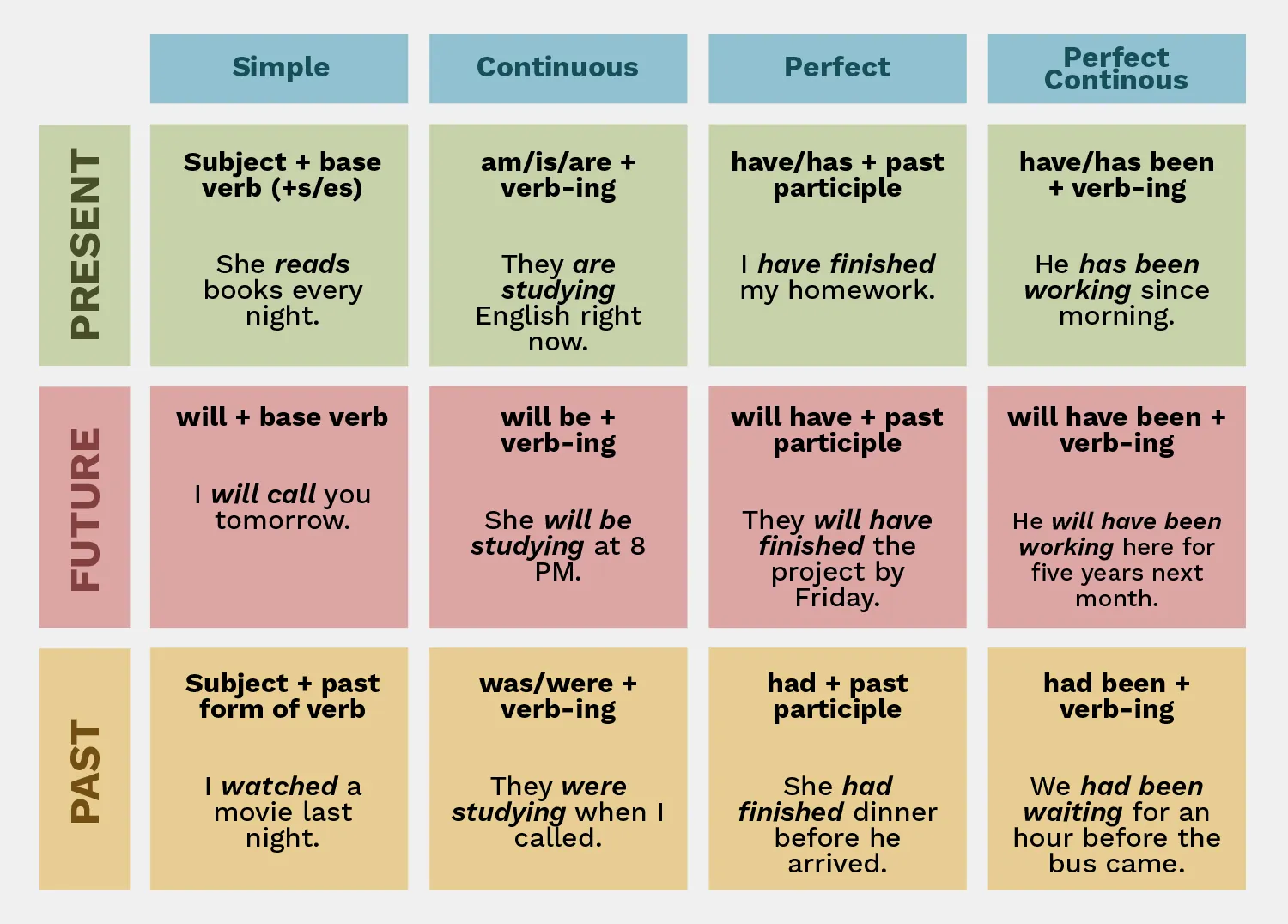
20 Examples of Present, Past, and Future Tenses
As promised in the title, here are 20 examples of present, past, and future tenses. These are simple sentences mixing all categories for practice. Try saying them out loud!
- Present Simple: I drink coffee every day.
- Present Continuous: She is dancing in the room.
- Present Perfect: We have visited the museum.
- Present Perfect Continuous: He has been painting the wall.
- Past Simple: They played games yesterday.
- Past Continuous: I was reading a book last night.
- Past Perfect: She had cooked dinner before guests arrived.
- Past Perfect Continuous: We had been hiking for hours.
- Future Simple: I will call you tomorrow.
- Future Continuous: They will be traveling next week.
- Future Perfect: He will have completed the project by Friday.
- Future Perfect Continuous: She will have been studying for three years.
- Present Simple: Birds fly south in winter.
- Past Simple: He fixed the car last weekend.
- Future Simple: We will meet at the park.
- Present Continuous: The kids are playing outside.
- Past Continuous: It was snowing when we left.
- Future Continuous: I will be working late tonight.
- Present Perfect: I have lost my phone again.
- Past Perfect: By then, they had already left.
These 20 examples of present past and future tenses cover a mix—count them: 7 present, 5 past, 4 future, and 4 mixed aspects. Rewrite them in your notebook with different verbs.

Common Mistakes Beginners Make with Verb Tenses
Even with a verb tenses list with examples for beginners, mistakes happen. Here’s how to avoid them:
- Mixing tenses in stories: Stick to past for narratives.
- Forgetting -s in present simple: “He eat” should be “He eats.”
- Using present perfect for specific past: Say “I ate yesterday,” not “I have eaten yesterday.”
- Overusing continuous: Not everything is “ongoing”. Use simple for habits.
- Irregular verbs: Practice the verb forms chart to remember “went” not “goed.”
Tips: Read simple books, watch English videos with subtitles, and practice daily. Apps like Duolingo can help.
How to Practice Verb Tenses Daily
To master past present future tenses and simple perfect continuous, try these:
- Journal: Write about your day using different tenses.
- Speak: Describe photos in present continuous.
- Quiz yourself: Change sentences from simple to perfect.
- Games: Play tense-matching card games.
With consistent practice, you’ll improve fast.
Master Verb Tenses and Boost Your English Skills
We’ve covered a complete verb tenses list with examples for beginners, including all 12 tenses, a verb forms chart, and 20 examples of present, past, and future tenses. From simple, perfect continuous to past, present, future tenses, you now have the tools to use them correctly. Remember, start small, practice often, and don’t fear mistakes, they’re part of learning.
If you’re an English beginner, bookmark this guide and refer back. For more English tips, check our posts on Instagram grammar basics. Happy learning!
Conquer the verb tenses! EnglishFact’s beginner courses make Past, Present, and Future Tenses easy to learn, helping you build confidence and speaking fluency quickly.
If you got questions about our grammar courses, please feel free to message us on WhatsApp or sign up for a FREE TRIAL ONLINE CLASS today!




